What is Insurance?
Insurance is defined as a cooperative device to spread the loss caused by a particular risk over a number of persons who are exposed to it and who agree to ensure themselves against that risk.
Table of Contents
Insurance Definition
The various definition of insurance can be classified into the following three categories:
General Definition of Insurance
The general definitions are given by the social scientists. Some of such definitions are given below:
The collective bearing of risks is insurance. – Sir William Bevridges
Insurance is a substitution for a small known loss for a large unknown loss by which may or may not occur. – Boon and Kurtz
Insurance is a cooperative form of distributing a certain risk over a group of persons who are exposed to it. – Ghosh and Agarwal
Thus, the insurance mean in the social sense is:
- A co-operative device to spread the risk.
- The system to spread the risk over a number of persons who are insured against the risk.
- The principles to share the loss of each member of the society on the basis of probability of loss to their risk.
- The method to provide security against losses to the insured.
Fundamental Definition of Insurance
Fundamental definitions are based on business oriented since it is a device providing financial compensation against risk or misfortune.
Insurance as a social device providing financial compensation for the effect of misfortune, the payments being made from the accumulated contributions of all parties in the scheme. – D.S.Hansell
Insurance is a social device whereby the uncertain risks of individuals may be combined in a group and thus made more certain, small periodic contributions by the individuals providing a fund, out of which, those who suffer losses may be reimbursed. – Riegel and Miller
Contractual Definition of Insurance
It is a contractual relationship to secure against risks. Some of such contractual definition are:
Insurance is a contract whereby one person, called the insurer, undertakes in return for the agreed consideration called premium, to pay to another person called the insured, a sum of money or its equivalent on specified event. – Justice Channel
Insurance is a contract in which a sum of money is paid to the assured as consideration of insurer’s incurring the risk of paying a large sum upon a given contingency. – Justice Tindall
Thus, the insurance mean in the legal or contractual sense is:
- Certain sum, called premium, is charged in consideration.
- Against the said consideration, a large sum is guaranteed to be paid by the insurer who received the premium.
- The payment will be made in a certain definite sum.
- The payment is made only upon contingency.
Characteristics of Insurance
- Insurance is a cooperative device to share the burden of risk which may fall on happening of some unforeseen events. Its most important nature is sharing of risks.
- The most important feature of every insurance plan is the higher degree of cooperation for mutual benefits and distributing a certain risk over a group of persons who are exposed to it.
- For the purpose of ascertaining the insurance premium, the volume of risk is evaluated, which forms the basis of insurance contract.
- The amount of payment in indemnity insurance depends on the nature of losses occurred, subject to a maximum of the sum insured.
- On the happening of specified event or in contingency the insurance company is bound to make payment to the insured.
For example: In life insurance, a fixed amount is paid on the happening of some uncertain event or on the maturity of the policy but in the case of fire, marine or accidental insurance, it is not necessary. In such cases, the insurer is not liable for payment of indemnity. - Insurance is a protection device to avoid or reduce economic risks or losses.
- Insurance is a plan which spreads the risks and losses of few people among a large number of people.
- Insurance is a device to transfer some economic losses.
- Insurance is a device of ascertaining of losses. By taking a life insurance policy, one can ascertain his future losses in term of money.
- Insurance is not charity because charity pays without consideration but in the case of insurance, premium is paid by the insured to the insurer in consideration of future payment.
- To spread the loss immediately, smoothly and cheaply, large number of persons should be insured against similar risk, thus keeping the premium rate at the minimum.
- Insurance is a legal contract between the insurer and insured. Insurer promises to compensate the insured financially within the scope of insurance policy and the insured promises to pay a fixed rate of premium to the insurer.
- Insurance is a plan of social welfare and protection of interests of the people.
- Insurance based upon fundamental principles like good-faith, insurable interest, contribution, indemnity, cause proximal, subrogation etc.
- The government of every country enacts the law governing insurance business so as to regulate and control its activities for the interest of the people. In India life insurance Act 1956 and General insurance Act 1972 are the major enactments in this direction.
Functions of Insurance
The functions of insurance can be classified into three parts:
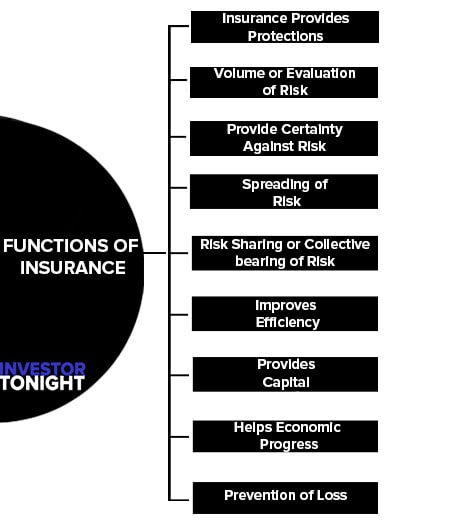
Primary Functions
- Insurance Provides Protections
- Volume or Evaluation of Risk
- Provide Certainty Against Risk
- Spreading of Risk
- Risk Sharing or Collective bearing of Risk
Insurance Provides Protections
The main function of the insurance is to provide protection against the probable chances of loss, future risk, accidents and uncertainty. The insurance cannot check the happening risk but can provide for losses at the happening of the risk.
Volume or Evaluation of Risk
Insurance determines the probable volume of risks by evaluating various factors that gives rise to risk. The risk is also evaluated on the basis of premium rate.
Provide Certainty Against Risk
Insurance provides certainty of payment at the uncertainty of loss. The uncertainty of loss can be reduced by better planning and administration. But, the insurance relieves the person from such difficult task. Insurance removes all these uncertainty and the assured is given certainty of payment of loss.
This may the reason that Riegel and Miller observe and then write that “the function of insurance is primarily to decrease the uncertainty of events”
Spreading of Risk
Insurance is a plan which spreads the risks and losses of few people among a large number of people. John Magee writes,” Insurance is a plan by which a large number of people associate them and transfer to the shoulders of all, risks attached to individuals”.
Risk Sharing or Collective bearing of Risk
Insurance is a device to share the financial loss of few among many others. The risk sharing in ancient time was done only at time of damage or death; but today, on the basis of probability of risk, the share is obtained from each and every insured in the shape of premium without which protection is not guaranteed by the insurer.
Secondary Functions
Improves Efficiency
The insurance eliminates worries and miseries of losses at death and destruction of property. The carefree person can devote his body and soul together for better achievement. It improves not only his efficiency, but the efficiencies of the masses are also advanced.
Provides Capital
The insurance provide capital to the society. The accumulated funds are invested in productive channel. Dinsdale observes, insurance relieves the businessmen and others from security investments, by paying small amount of premium against larger risk and uncertainty.
There is no need for them to invest separately for security purpose and this money can be invested in other activities.
Helps Economic Progress
The insurance by protecting the society from huge losses of damage, destruction and death, provides and initiative to work hard for the betterment of the masses. The next factor of economic progress, the capital, is also immensely provided by the masses.
The property, the valuable assets, the man, the machine and the society cannot lose much at the disaster.
Prevention of Loss
Insurance cautions individuals and businessmen to adopt suitable device to prevent unfortunate consequences of risk by observing safety instructions; installation of automatic sparkler or alarm systems, etc.
Prevention of losses cause lesser payment to the assured by the insurer and this will encourage for more savings by way of premium. Reduced rate of premiums stimulate for more business and better protection to the insured.
Other Functions
There are some indirect or others functions of insurance which indirectly provide economy benefit to the insured people.
- Insurance serves as compulsory way of savings or investment and it restricts the unnecessary expenses by the insured.
- The country can earn foreign exchange by way of issue of marine insurance policies.
- Insurance makes the foreign trade risk free through different types of policies.
- Insurance provide social security to people not only at the time of death but also provide assistance to the insured at the time of sickness, old age, maternity etc.
Types of Insurance
Types of insurance are:
Life Insurance
Life insurance is different from other insurance in the sense that, here, the matter of insurance is life of human being. The insurer will pay the fixed amount of insurance at the time of death or at the expiry of certain period.
Life insurance may be defined as a contract in which the insurer, in consideration of a certain premium, either in a lump sum or by other periodical payments, agrees to pay the assured, or to the person for whose benefit the policy is taken, the assured sum of money, on the happening of a specified event contingent on the human life.
At present, life insurance enjoys maximum scope because the life is the most important property of the society or an individual. Each and every person requires insurance. This insurance provides protection to the family at the premature death or gives adequate amount at the old age when earning capacities are reduced.
Under personal insurance a payment is made at the accident. The insurance is not only a protection but is a sort of investment because a certain sum is returnable to the insured at the death or at the expiry of a period.
Non-Life Insurance
In the non-life insurance included general and miscellaneous insurance like fire insurance, marine insurance, cattle insurance, crop insurance and flood insurance etc.
General Insurance
General insurance business refers to fire, marine and etc insurance business whether carried on singly or in combination with one or more of them, but does not include capital redemption business and annuity certain business.
Marine Insurance
Marine insurance provides protection against loss of marine perils. The marine perils are collision with rock, or ship, attacks by enemies, fire, robbers, thieves, captures, jettisons, barratry and etc. These perils cause damage, destruction or disappearance of the ship and cargo and non-payment of freight.
There are different types of marine policies known by different names according to the manner of their execution or the risk they cover. They are: voyage policy, time policy, and valued policy, unvalued policy, floating policy, wager or honors policy.
Fire Insurance
Fire insurance is a contract to indemnity the insured for distribution of or damage to property caused by fire. The insurer undertakes to pay the amount of insured’s loss subject to the maximum amount stated in the policy. Fire insurance is essentially a contract of indemnity, not against accident, but against loss caused by accident. War risk, turmoil, riots, etc, can be insured under this insurance too.
Social Insurance
Social insurance has been developed to provide economic security to weaker sections of society who are unable to pay the premium for adequate insurance. Some are these sickness insurance, death insurance, disability insurance, unemployment insurance and old-age insurance.
Property Insurance
The Property of an individual and of the society is insured against the loss of fire and marine perils, the crop is insured against unexpected decline in production, unexpected death of the animals engaged in business, break-down of machines and theft of the property and goods.
Liability Insurance
The liability insurance covers the risks of third party, compensation to employees, liability of the automobile owners and reinsurances.
Miscellaneous Insurances
The process of fast development in the society gave rise to a number of risks or hazards. To provide security against such hazards, many others types of insurance also have been developed.
The important among them are:
- Crop Insurance
- Burglary Insurance
- Fidelity Insurance
- Flood Insurance
- Cattle Insurance
- Cash in Transit Insurance
- Vehicle Insurance
- Personal accidents Insurance
- Legal liability Insurance
Types of Insurance Companies
Insurance companies can be categorized into two main divisions which are classified as follows:
- General Insurance Companies: They provide all types of insurance apart from life insurance i.e., fire insurance, marine insurance, vehicle insurance etc.,
- Life Insurance Companies: The companies, dealing with life insurance, pension products and annuities are life insurance companies.
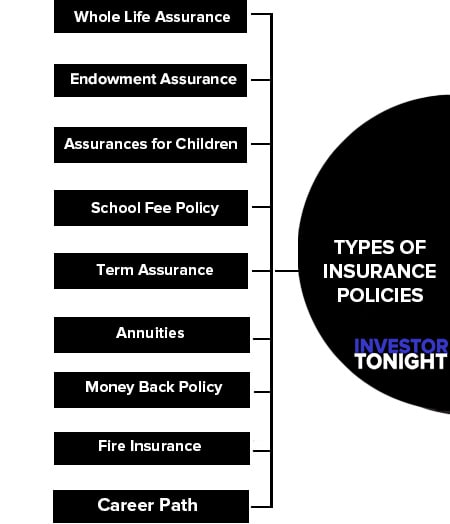
Types of Insurance Policies
Insurance provides compensation to a person for an anticipated loss to his life, business or an asset. Insurance is broadly classified into two parts covering different types of risks:
Life Insurance
“A contract in which the insurer undertakes to a pay a certain sum of money to the insured, either on the expiry of a specified period or on the death of the insured, in consideration of payment of ‘premium’ for a certain period of time, is known as ‘life insurance”.
It is otherwise called as ‘Life Assurance’. Generally, the tenure of Life insurance policy is long-term in nature; it may either be for a certain period or the whole life period of the insured. Insurance against risk to one’s life is covered under ordinary life assurance.
Ordinary life assurance can be further classified into several types:
- Whole Life Assurance
- Endowment Assurance
- Assurances for Children
- School Fee Policy
- Term Assurance
- Annuities
- Money Back Policy
Whole Life Assurance
In whole life assurance, insurance company collects premium from the insured for whole life or till the time of his retirement and pays claim to the family of the insured only after his death.
Endowment Assurance
In case of endowment assurance, the term of policy is defined for a specified period say about 15, 20, 25 or 30 years. The insurance company pays the claim to the family of the assured in the event of his death, within the policy’s period or in an event of the assured surviving the policy’s period.
In the event of the insured surviving beyond the coverage/specified period, the maturity value/sum assured along with bonus will be paid to the insured himself.
Assurances for Children
Child’s Deferred Assurance: Under this policy, the insurance company pays the claim to the insured on the maturity date of the policy, which is calculated to coincide either with the date of child’s eighteenth or twenty-first birthday or attaining majority.
The policy holder may either claim the payment on the date of maturity period or continue the insurance coverage. If the parent dies before the option date, the policy remains continued until the option date without paying a premium for the remaining period. Suppose, the child dies before the option date, the parent gets back the premium plus bonus.
School Fee Policy
School fee policy can be availed by affecting an endowment policy on the life of the parent with the sum assured, payable in installments over the schooling period of their children.
Term Assurance
Term assurance is life insurance which provides coverage at a fixed rate of payments for a limited period of time in respect of the term offered by the assured. In case, the insured dies during the term, the death benefit will be paid to the beneficiary.
If the insured survives after that period expires, either he has to pay additional premium for obtaining further coverage or he has to forgo coverage. It is the least expensive way to purchase a substantial death benefit on a coverage amount over a specific period of time.
Annuities
Annuity is a contract under which the insurer (insurance company) promises to pay the insured a series of payments until the insured’s death. The insured make the premium payment in the mode of either lump sum or installments to the insurer.
Generally, life annuity is chosen by a person having surplus wealth and wants to use this money after his retirement. The annuities can be further classified into two types, which are as follows:
- Immediate Annuity: It means that the insured pays a lump sum amount (purchase price) to the insurer and in turn the insurer promises to pay him a specified sum on a monthly/quarterly/halfyearly/ yearly basis.
- Deferred Annuity: A deferred annuity can be purchased either by way of installments or by paying a single premium. The insured receives the annuity after the deferment period.
Money Back Policy
A money back policy is issued for a particular period, and the sum assured is paid through periodical payments to the insured, spread over this time period. In case of death of the insured within the term of the policy, full sum assured along with bonus accruing on it, is payable by the insurance company to the nominee of the deceased. Generally, Money
General Insurance
General insurance is also known as non-life insurance. It is normally meant for a short-term period of twelve months or less. In recent years, insurance companies are entering long-term insurance agreements also and the period would not exceed five years.
General insurance can be classified into the following categories:
Fire Insurance
Fire insurance provides protection against damage to property caused by accidents due to fire, lightning or explosion. Fire insurance also includes damage caused due to other perils like storm, tempest or flood, burst of pipes, earthquake, riot, civil commotion, malicious damage, explosion, impact (e.g. – aircraft).
Marine Insurance
Hull, cargo and freight are the three basic risk covering area for Marine insurance. Those risks areas are exposed to are collectively known as “Perils of the Sea”. These perils include theft, fire, collision etc.
- Marine Cargo: Marine cargo policy provides protection to the goods loaded in a ship against all perils between the departure and arrival to warehouse. Therefore, marine cargo covers carriage of goods by sea as well as transportation of goods by land.
- Marine Hull: Marine hull policy provides protection against damage to ship caused due to the perils of the sea. In the event of any loss sustained due to collisions at sea, Marine hull policy covers only 3/4th liability of the hull owner (ship-owner) and the remaining 1/4th of the liability is looked after by associations formed by ship owners for the purpose.
Miscellaneous
Miscellaneous insurance covers all types of general insurance, except fire and marine insurances. Some of the examples of general insurance are motor insurance, theft insurance, health insurance, personal accident insurance, money insurance, engineering insurance, etc.
Importance of Insurance
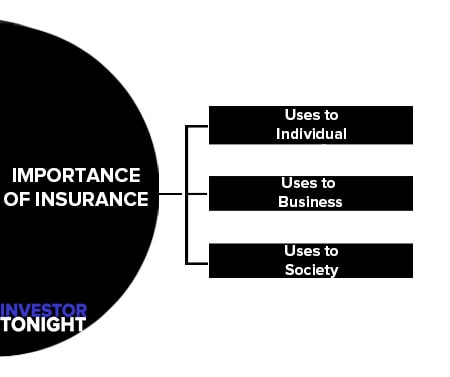
Uses to Individual
- Insurance provides security and safety
- Insurance affords peace of mind
- Insurance protects mortgaged property
- Insurance eliminates dependency
- Life insurance encourage saving
- Life insurance provides profitable investment
- Life insurance fulfills the needs of a person like family needs, old age needs, re-adjustment needs, need for education, marriage, insurance needs for settlement of children and clean up funds.
Uses to Business or Industry
- Uncertainty of business losses is reduced
- Key man indemnification
- Enhancement of credit
- Business continuation
- Welfare of employees
Uses to Society
- Wealth of the society is protected
- Economic growth of the country
- Reduction in inflation
Limitation of Insurance
Insurance has certain limitations and on account of such limitations, the benefits of insurance could not be availed in full. Limitation of insurance are:
- Only pure risks can be insured and speculative risks are not insurable.
- Due to higher premium rates certain category of people cannot avail the advantage of insurance.
- It is difficult to control over moral hazards in insurance because some people mis- utilize the insurance plans for their self- interest by claiming false claims from insurance companies.
- In certain cases like unemployment insurance, insolvency of banks etc. cooperation of government is required.
- All the pure risks are also not insured. For example insurer does not take any interest to accept a proposal of a person whose suffer from cancer.
- The private insurers are not permitted to insure specified types of risks like bankruptcy of banks, unemployment etc.
- Insurance against the risk of a single individual or a small group of persons are not advisable since it is not practicable due to higher cost involved.
- The event cannot be valued in terms of money, such risks are not insurable.
- Insurance is possible only when the insured has insurable interest in the term of financial interest in the subject matter of insurance.
- Main object of insurance is to provide security against the risks. It is not a profitable investment.
Read More Articles
- What is Financial Management?
- What is Financial Statements?
- What is Financial Statement Analysis?
- What is Ratio Analysis?
- What is Funds Flow Statement?
- What is Cash Flow Statement?
- What is Working Capital?
- What is Cost of Capital?
- What is Capital Budgeting?
- What is Dividend Policy?
- What is Cash Management?
- What is Depository?
- What is Insurance?
- What is Financial System?
- International Financial Reporting Standards
- Stability of Dividends
- What is Factoring?
- Determinants of Working Capital
- Public Finance
- Public Expenditure
- What is Public Debt?
- Classification of Public Debt
- Federal Finance
- Effect of Public Debt
- Expenditure Cycle
Helpful