What is Public Issue?
When a company raises funds by selling or issuing its shares to the public through issue of offer document/prospectus, it is called a public issue.
Table of Contents
Every Company needs funds for its business. Funds requirements can be for the short term or for long term. To meet short-term requirements, the company may approach banks, lenders and may even accept fixed deposits from public/shareholders.
To meet its long-term requirements, funds can be raised either through loans from lenders, Banks, Institutions, etc. These loans carry a financial burden as an interest to be payable periodically. Another option to raise long-term capital is through public issues. Public issue means raising funds from the public.
Types of Public Issue
Initial Public Offer (IPO
When a company makes a public issue for the first time, the public issue is called as initial public offer (IPO)
Further public offer (FPO)
When a company makes another public issue to raise capital, it is called further public /follow-on offer (FPO).
Advantages of Public Issue
- Money non-refundable except in the case of winding up or buy back of shares.
- No financial burden i.e. no fixed rate of interest payable. However, in order to service the equity, dividend may be paid.
- Enhance shareholders’ value if the Company performs well.
- Greater Transferability.
- Trading and Listing of securities at stock exchanges.
- Better liquidity of securities.
- Helps building reputation of promoters, Company and its products/services, provided the Company performs well.,
Disadvantages of Public Issue
- Time consuming process.
- Expensive
- Several legal formalities
- Involvement of many intermediateries.
- Transparency requirements and public disclosure of information may lead to lack of privacy.
- Continuous compliance of provisions of listing agreement and other legal requirements.
- Constant scrutiny of performance by investors.
- May lead to takeover of the company
- Securities of the Company may be made subjective to speculative attacks.
Intermediaries in IPO
Many intermediaries are involved in connection with the public issue. Following are the intermediaries who have to be registered with SEBI and must have valid certificate from SEBI to act as an intermediaries:
• Merchant Bankers
• Registrar & Share Transfer Agents
• Bankers to the issue
• Underwriters
• Stock Brokers and sub-brokers
• Depositories
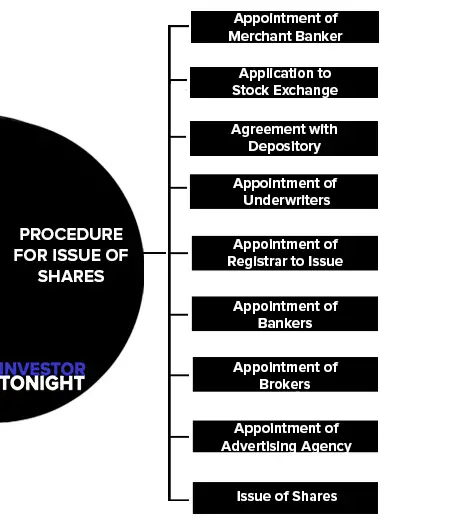
- Appointment of Merchant Banker
- Application to Stock Exchange
- Agreement with Depository
- Appointment of Underwriters
- Appointment of Registrar to Issue
- Appointment of Bankers
- Appointment of Brokers
- Appointment of Advertising Agency
- Issue of Shares
Appointment of Merchant Banker
The first thing that company management must do when they have taken a decision to go public is to find a Merchant Banker who will manage the entire process of public issue. Merchant Banker is a financial intermediary/institution who is an expert in managing public issue, dealing with SEBI Regulations and Registrar of Companies on public issue. Following are the services rendered by the Merchant Banker with regard to Public Issue:
- Advisory Service: The Merchant Banker advises the issuing company about size, mode and timing of public issue. The issuing company can finalise its decision based on this advice.
- Preparation of Basic Documents: It includes the following:
- Prospectus: The merchant banker first prepares the draft prospects (red herring prospectus) and at later stage of issue prepares the final Prospectus. Prospectus is a document by way of which the investor gets all the information pertaining to the issuing company in which they are going to invest.
It gives the detailed information about the Company, Promoter/Directors, group companies, capital structure, terms of the present issue, details of proposed project, particulars of the issue etc. On behalf of the company, these are filed with SEBI and Registrar of Companies by the Merchant Banker. - Memorandum of Understanding (MOU): It is contract between the issuing company and the Merchant Banker. It defines the rights, duties and obligations of the merchant banker with regard to public issue.
- Due Diligence Certificate: It is a declaration made by the Merchant Banker that all the information furnished by the company is reliable and all SEBI guidelines are duly fulfilled for the public issue. If SEBI is satisfied with information, it will suggest the Merchant Banker to prepare the final prospectus.
- Prospectus: The merchant banker first prepares the draft prospects (red herring prospectus) and at later stage of issue prepares the final Prospectus. Prospectus is a document by way of which the investor gets all the information pertaining to the issuing company in which they are going to invest.
- Appointment of other Merchant Bankers and Allocation of Responsibilities: If more than one Merchant Banker required for the public issue, the appointment is made by the main Merchant Banker and the main Merchant Banker is called as Lead Manager. Further, all the responsibilities of public issue are distributed among the Merchant Bankers
Application to Stock Exchange
After the public issue, the shares are to be listed/included in recognised stock exchanges for trading. For this, an application to be filed with recognised stock exchanges seeking permission for listing. Listing is allowed by the stock exchange when issuing company fulfils all the regulations of listing issued by the stock exchanges.
Agreement with Depository
Today, the shares are allotted to the investors in an electronic form. This requires opening of Demat Account with depositories and all the shares allotted are credited to Demat Account.
A depository is an organization where the securities of an investor are held in electronic form. The issuing company enters into contract with the Depositories for allotment of shares. There are two depositories in India who maintain the Demat Account:
- National Securities Depository Limited (NSDL) promoted by National Stock Exchange (NSE)
- Central Depository Services Limited (CDSL) promoted by Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE)
Appointment of Underwriters
Underwriter is a financial intermediary who guarantees the subscription/purchase of shares if public does not subscribe to the required quantity of shares. The Lead Manager verifies the net worth and outstanding commitments of the underwriter appointed and send this information as a report to SEBI.
Appointment of Registrar to Issue
The Registrar to Issues a bank or a similar company generally performs the following record keeping activities by coordinating with Lead Manager:
- Printing and processing of IPO applications
- Advising the company to appoint Bankers to the Issue
- Despatching application to banks and brokers for distribution to investors
- Monitoring subscription when public issue is open and collecting information from banks
- Collecting application when subscription is closed
- Tabulating the details of subscription
- Allotment of shares to applicants based on SEBI guidelines
- Process of refunds through ECS or cheque
- Transfer allocated shares to Demat accounts of investors
Appointment of Bankers
The issuing company does not directly collect Application money from the investors. The issuing company with the help of Lead Manager and Registrar to the Issue appoints Bankers to the Issue. A separate bank account is opened with Bankers to the Issue to collect application money from investors through its branches.
Appointment of Brokers
When issue of share process is to start, the brokers are appointed by the company management, in consultation with merchant bankers to the issue. Broker is the member of the stock exchange who has large contact of investors. Merchant bankers appoint a broker of huge reputation and these brokers ensures the sale of shares to the public.
Appointment of Advertising Agency
Appointment of Advertising Agency is made for marketing of public issue. Advertisements are given both print and electronic media to gain wide publicity for the public issue. The Road Shows are also organised to create interest among prospective investors. In the advertisement, date of opening and closing of subscription list, number of shares offered, price band, basis of allotment are highlighted.
After the appointment of various competent authorities and finalisation of prospectus, listing agreement, applications etc., the steps given below are followed in the public issue of shares:
- Filing Prospectus: The Lead Manager shall arrange to file the final prospectus with SEBI, Registrar of Companies and Stock Exchange
- Press Conference: The press conference/investor meet is arranged to announce the public issue of shares
- Despatch of Application Forms: The Registrar to the Issue shall arrange for the distribution of application forms to the bankers, brokers etc.
- Opening of Subscription List: The subscription list is kept open for minimum of 3 days and maximum of 7 days during which public can apply for the public issue of shares. The bankers accept the application along with money and inform the Registrar the status of response on a daily basis.
- Closure of Subscription List: The company announces the closure of public issue through the media. After closure, the bankers send the applications to the Registrar to the Issue.
- Allotment of Shares: The Registrar allots the shares in consultation with Issuing Company, SEBI and Stock Exchanges. The allotment is made to the Demat Account of the investors and refund of excess application money received is also undertaken.
- Listing of Shares: Finally shares are listed in the stock exchanges where listing agreement is made and company informs the SEBI about the listing. Thereafter, regular trading in shares are undertaken.
Methods of Pricing Public Issue
Fixed Price Method
In an Initial public offering (IPO), if the shares are offered at a fixed price, such is issue is known as Fixed price issue. This is the second most preferred way of Initial public offering. In the offer document, the issuer has to give the reasoning and proper justification for the price fixed.
Generally, companies go for fixed price issue only when the management is of the opinion that a fair price can be decided among them without having tested in the market like in the case of book building.
Book Building Method
It is a process used in IPOs for efficient price discovery and determination of quantity of shares to be issued. The price at which securities would be offered is not known initially. It is known only after the closure of the book building process.
It is a common method of marketing of new issues in several developed countries. In book building method, the market discovers the price instead of the company determining the price.
Book Building vs Fixed Price Method
The main difference between the book building method and the fixed price method is that in the former, the issue price not decided initially. The investors have to bid for the shares within the price range given. The issue price is fixed on the basis of demand and supply of the shares.
On the other hand, in the fixed price method, the price is decided right at the start. Investors cannot choose the price. They have to buy the shares at the price decided by the company. In the book building method, the demand is known every day during the offer period, but in fixed price method, the demand is known only after the issue closes.